Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of driving targeted traffic to your website by improving its visibility in organic (unpaid) search engine rankings. The primary objective of SEO is to rank your website higher in search results for keywords relevant to your business.
Table of Contents
Higher rankings mean more traffic, which can lead to increased conversions, whether that’s sales, sign-ups, or another desired action.

SEO encompasses both the technical elements of your website and content-focused best practices, ensuring search engines like Google can efficiently find, understand, and index your site. Additionally, it helps improve the user experience for your visitors.
Key SEO activities include:
- Creating valuable content that aligns with user intent.
- Optimizing content for specific keywords to ensure relevance.
- Building backlinks to improve site authority.
The greatest advantage of SEO is its potential to deliver “free” traffic consistently. Once your site ranks for a keyword, you can benefit from ongoing traffic month after month.
This guide will explore:
- Why SEO is essential.
- How SEO works.
- Different types of SEO you can implement for improved visibility.
Why is SEO Important?
In simple terms: search traffic drives massive opportunities.
This holds for businesses across all industries and personal websites or blogs.
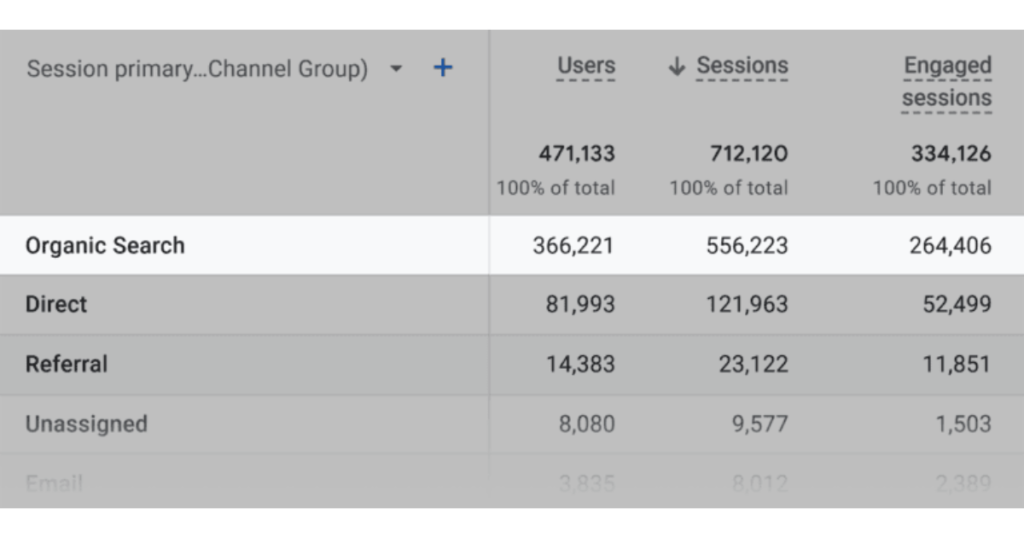
For example, on our own site, a significant portion of traffic—over 78%—comes from organic search. This demonstrates how critical SEO can be for sustained growth.
Let’s consider a real-world scenario:
Suppose you own a party supply business. According to Ubersuggest’s Keyword Overview tool, around 33,000 people in the U.S. search for “party supplies” every month.
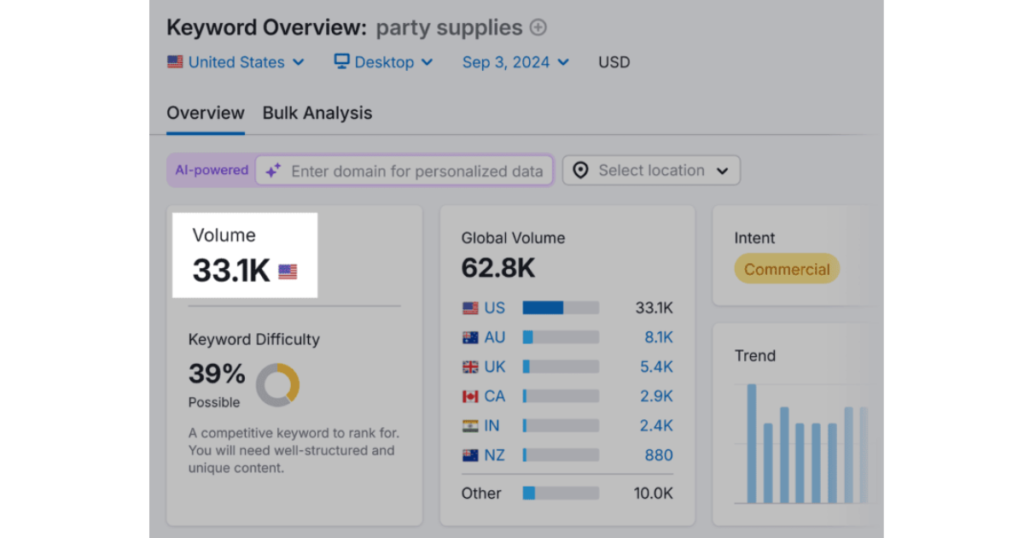
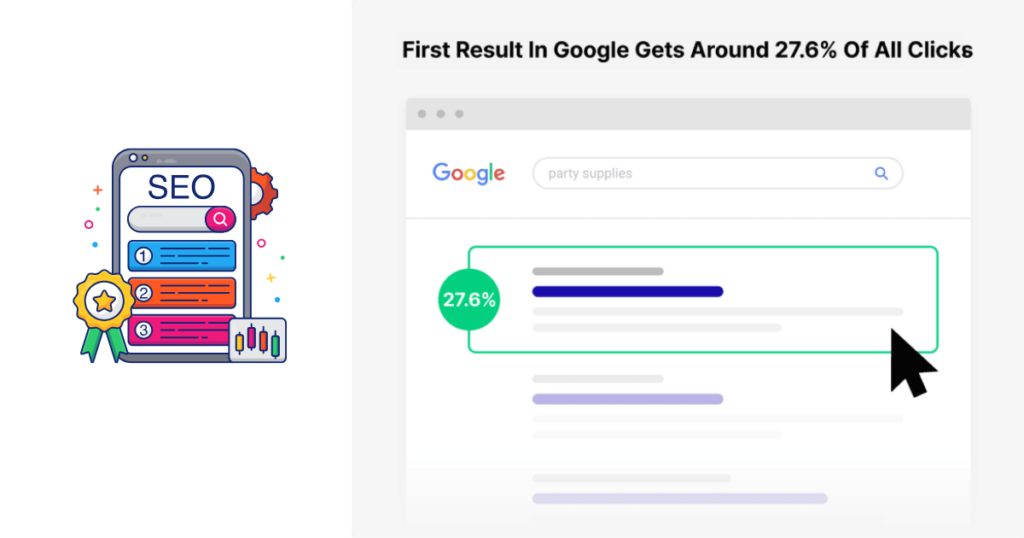
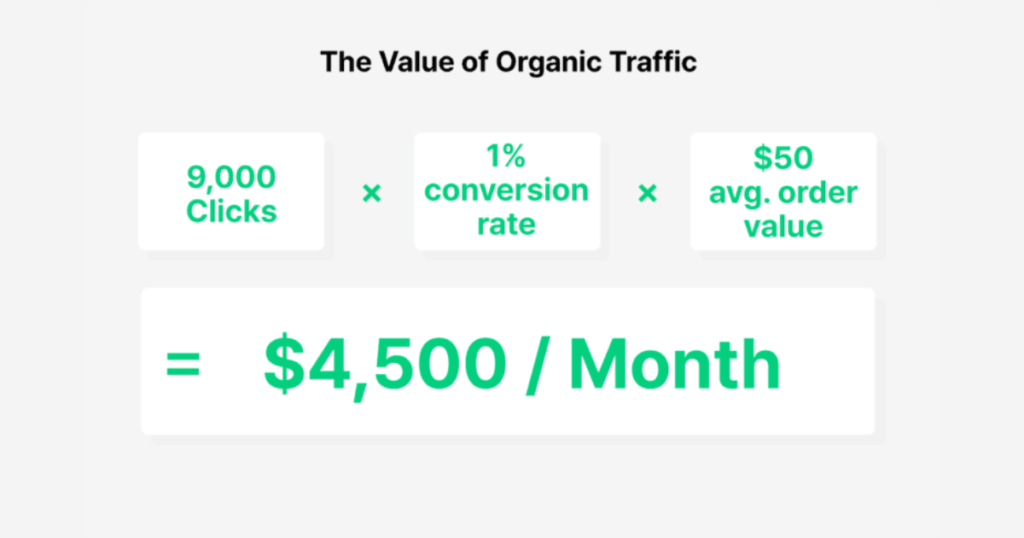
The top result on Google typically captures 27.6% of all clicks, translating to roughly 9,000 visitors monthly—from just one keyword.
Using Ubersuggest, you can also estimate the potential traffic your site could earn if it ranks in the top positions. The Potential Traffic metric considers factors like your domain authority, estimated click-through rate, and competition.
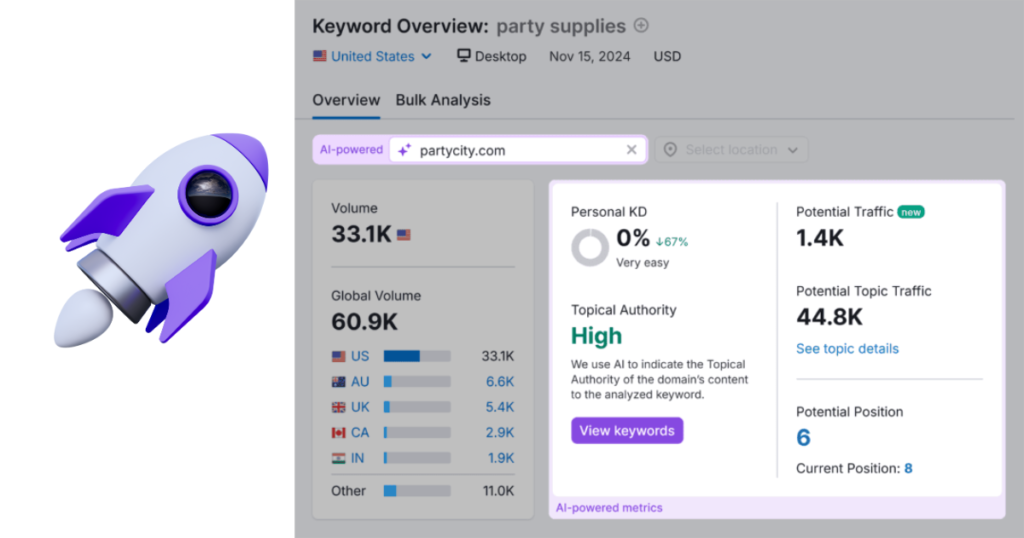
But how valuable is this traffic?
The average advertiser spends about $1 per click for the term “party supplies.” So, if you rank organically and attract 9,000 visitors, that traffic would be worth $9,000 per month—and it’s essentially “free.”
Imagine your site is optimized for dozens—or even hundreds—of similar keywords. The cumulative traffic and revenue could be substantial.
For example, converting just 1% of those 9,000 visitors into paying customers, with an average order value of $50, could generate $4,500 in monthly revenue from one post.
Organic vs. Paid Search Results
When you perform a search, the results page is typically divided into two sections:
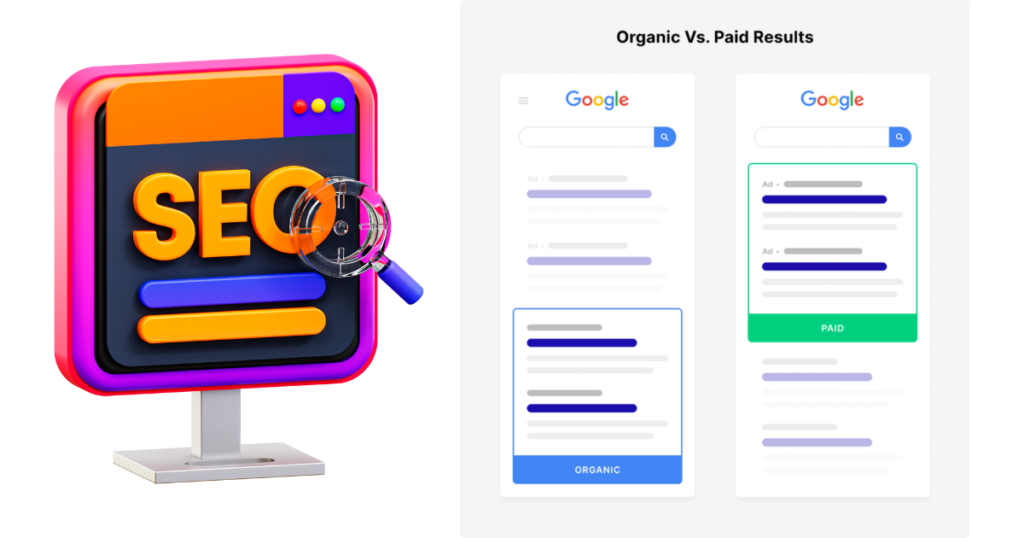
- Organic Results
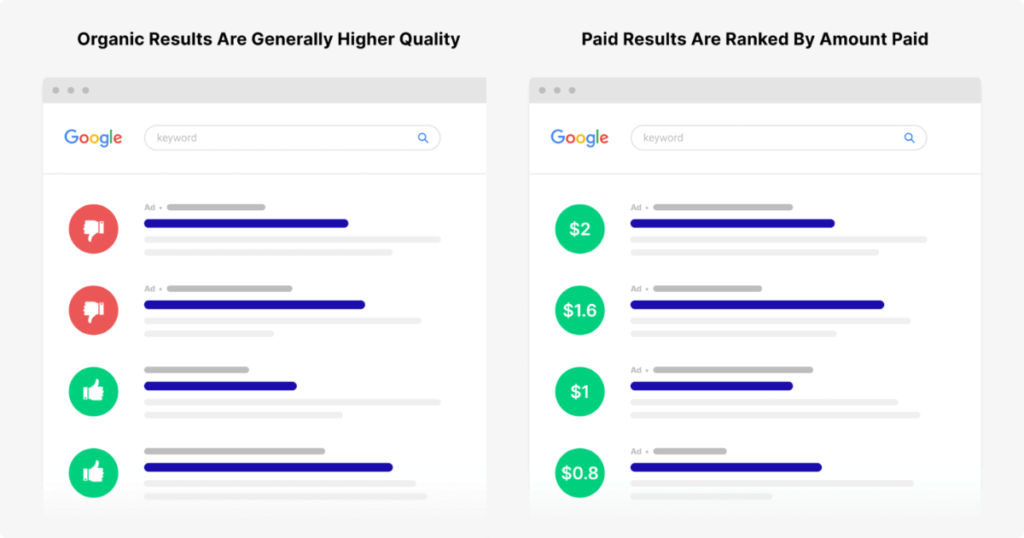
- These are unpaid listings determined by Google’s ranking algorithms.
- Factors such as relevance, trustworthiness, and authority influence organic rankings.
- Paid Results
- These are advertisements that appear at the top or bottom of search results.
- Paid ads operate on a completely different system and aren’t influenced by SEO strategies.
For this guide, we’ll focus exclusively on organic results, as they’re the cornerstone of SEO.
SEO vs. SEM
While SEO targets organic traffic, Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a broader strategy that includes both SEO and paid search campaigns.
If you want to dive deeper into the differences, check out our dedicated guide to SEO vs. SEM for a comprehensive breakdown.
How Search Engines Work
Have you ever wondered how you ended up on this page? Perhaps you searched for something like “What is SEO?” and let the search engine do the rest. Behind the scenes, a sophisticated algorithm delivered what it deemed the “best” result to match your query.
When you type a search query into Google—or any other search engine—it instantly sifts through its vast index, containing hundreds of billions of pages, to find results that most accurately and effectively answer your question.
How Does Google Determine the “Best” Result?
While Google keeps its precise ranking metrics (known as ranking factors) under wraps, we do have insight into its overall process. Here’s a closer look at how search engines like Google analyze and rank content:
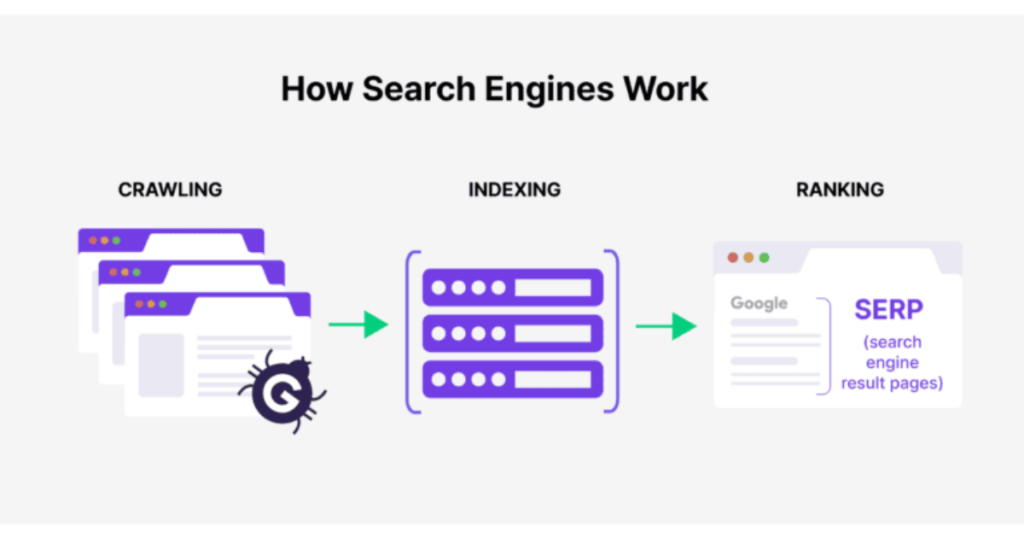
- Crawling
Google deploys crawlers (also known as bots or spiders) to explore the internet. These bots navigate websites, following internal and external links, and gathering information about page content. - Indexing
Once the bots crawl a page, they evaluate its content—including text, images, videos, and meta tags—to determine its relevance. If deemed useful, the page is added to Google’s index, a massive database of web pages. - Ranking
Finally, Google’s ranking algorithm comes into play, analyzing various factors to determine which pages should appear in search results—and in what order.
Key Factors That Influence Search Rankings
While Google’s algorithm is complex, here are three core factors that we know impact rankings:
1. Relevancy
Relevance measures how closely a page’s content matches the intent behind a user’s query. For instance, if you search for “chocolate chip cookie recipes,” you wouldn’t want results about car tires.
However, relevance alone isn’t enough. With potentially thousands or even millions of relevant pages for any given search term,
Google relies on additional factors to decide which pages deserve the top spots.
2. Authority
Authority reflects a website’s trustworthiness and credibility in its niche. While Google hasn’t explicitly defined “authority,” links play a significant role in determining it.
Backlinks—links from other websites to your page—endorse your content’s value. In particular, backlinks from prominent, reputable sites signal to Google that your content is authoritative.

For example, if a page on your website receives multiple high-quality backlinks from trusted sources, it’s more likely to rank higher.
3. Usefulness
Even if a page is relevant and authoritative, it must also be useful to earn a top spot in search results.
Usefulness refers to how well a page satisfies user intent. Does it provide actionable, engaging, and well-organized content? Is the information presented in a way that’s easy for the target audience to understand?
Let’s say you’re researching the Paleo Diet. Imagine two scenarios:
- Result A: The content is written by a leading expert in Paleo nutrition. It has plenty of backlinks and is highly detailed. But the page is poorly organized and packed with jargon, making it difficult for readers to follow.

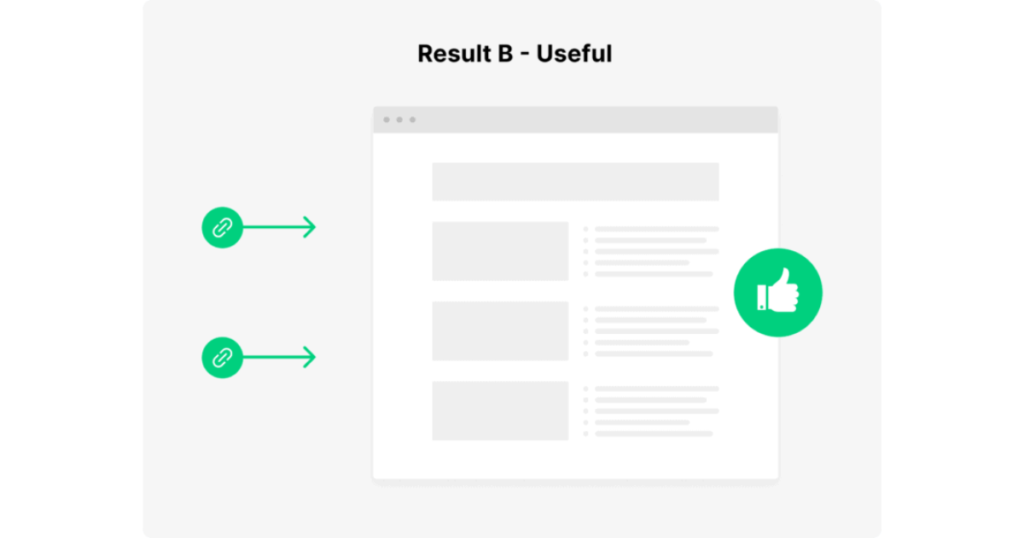
- Result B: Another page on the same topic is well-structured, concise, and answers common questions.
Which one would you prefer? Google prioritizes content that not only demonstrates expertise but also provides an excellent user experience.
Behind the Curtain
Search engines like Google are constantly refining their algorithms to provide users with the most accurate, helpful, and authoritative results possible. Understanding these key factors—relevance, authority, and usefulness—can help you create content that ranks well and delivers real value to your audience.
In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into strategies to improve your authority, including how to earn high-quality backlinks. Stay tuned!
Usefulness and User Experience
Now, imagine another scenario:
Result B is written by someone relatively new to the Paleo Diet. Their website lacks the extensive backlinks and authority of Result A. However, their content is organized into clear, distinct sections, written in a way that anyone can understand.
Even though Result B doesn’t have as much authority, its user-friendly structure makes it more useful to both visitors and search engines. In some cases, it might even outrank Result A, despite having fewer backlinks.
Why?
Google likely evaluates usefulness based on user experience signals—how people interact with the search results. If a page gets a lot of clicks, and users stay on it for a significant amount of time, Google may boost its ranking.
While many factors influence search rankings, creating content that is relevant, authoritative, and aligned with search intent gives you a strong foundation for success.
Types of SEO
To help your content perform well in search rankings, it’s essential to understand and apply the three main types of SEO:
Other specialized forms of SEO, like local SEO and video SEO, can also be important depending on your niche, but we’ll focus on these three core types.
1. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to optimizing your website’s content to make it relevant, engaging, and accessible to both search engines and users. It involves creating detailed, useful, high-quality content targeting specific search phrases.
Key components of on-page SEO include:
a. Keyword Optimization
Search engines like Google analyze your content for specific words and phrases—your keywords—to understand what it’s about.

When the same term appears consistently across your page, Google recognizes its relevance.
However, moderation is key. Overusing your keyword—known as keyword stuffing—can lead to penalties. Instead, focus on:

- Naturally incorporating your target keyword into your content.
- Using synonyms and variations of your keyword to increase relevance for related searches.
For example, let’s say your target keyword is “SEO tools.” You might also include related terms like “keyword research,” “backlink analysis,” or “content optimization.” These are often referred to as LSI keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing keywords), which help Google better understand the context of your content.
b. Internal Linking and Media
Incorporate valuable internal links to guide users to related content on your site. Additionally, use helpful images, infographics, and videos to enhance user experience and engagement.
Example:
In one of my posts, I optimized for the keyword “outreach tools.” By including the target keyword in the title tag, headings, and throughout the body text, I achieved a top ranking for that term.
But I didn’t stop there. By adding variations like “backlink analysis” and “link-building strategies,” the same page ranks for multiple related keywords, increasing its traffic potential significantly.
Choosing the Right Keywords
Unsure which keywords to target? Start by entering a broad term related to your business into Ubersuggest’s Keyword Magic Tool. This tool provides thousands of keyword ideas, including variations, search volumes, and competition levels, making it easier to choose terms that align with your content goals.
Note: A free Ubersuggest account gives you up to 10 credits per day with this tool. Or you can use this link to access a 7-day trial on a Ubersuggest subscription.
By strategically optimizing your content for these keywords, you can create a solid on-page SEO strategy that improves visibility and attracts valuable traffic.
Next, let’s explore the technical side of SEO!
Maximize the Impact of Keywords in Strategic Places
One of the most impactful places to include your target keyword is in your title tag, which directly influences how your page ranks in search results.
Why?
The title tag acts as a summary of your page’s content. When you include your keyword here, you’re signaling to Google that your page is directly relevant to that term.
For example, when I created a list of SEO tips, my target keyword for the page was, naturally, “SEO Tips.” So, I made sure my title tag explicitly included that keyword:
“10 Actionable SEO Tips to Boost Your Rankings Today”
Don’t Forget the URL
While not as critical as the title tag, including your keyword in your URL can help both Google and users understand what your page is about.
For instance, a URL like:
example.com/seo-tips
is clearer and more relevant than something vague like:
example.com/page-1234.
Should You Change Existing URLs?
In most cases, it’s best to leave your existing URLs as they are—even if they’re not optimized. Changing them can disrupt your rankings unless you implement 301 redirects to guide users and search engines from the old URL to the updated one.
Instead, focus on creating SEO-friendly URLs for future content.
Optimize Your Meta Descriptions for Click-Throughs
Your meta description may not directly impact rankings, but it’s invaluable for encouraging clicks. A well-crafted description entices users to choose your result over others.
For example:
“Learn the top SEO tips to boost your website’s rankings. Actionable strategies, tools, and insights to grow your organic traffic—fast!”
This description is engaging, highlights value, and aligns with the search intent.
Use Keywords in Your Meta Description
While keywords in the meta description won’t improve rankings, they often appear bolded in search results, helping your listing stand out.
Pro Tip: Leverage Yoast SEO
If you’re using WordPress, the Yoast SEO plugin simplifies the process of setting up title tags and meta descriptions. It’s a must-have tool for fine-tuning your on-page SEO.
Image Optimization
Search engines are improving at understanding images, but they still rely on metadata like filenames, alt text, and titles to grasp an image’s content. Here’s how to optimize your images effectively:
- Descriptive Filenames
Rename your image files with clear, descriptive terms.
For example, instead of IMG00123.jpg, use mobile-seo-guide-comments.png. - Alt Text
Write concise but descriptive alt text that explains the image. This helps search engines and improves accessibility for visually impaired users. - Image Titles
While less critical, you can copy and paste your alt text into the title field for consistency.
Create a Stellar User Experience (UX)
Even if your content is optimized, poor user experience will hurt your rankings. Google rewards sites that are easy to navigate, visually appealing, and helpful to users.
Tips for an Awesome UX:
- Use short paragraphs and sentences for better readability.
- Add visuals, like charts or infographics, to break up text and provide more context.
- Organize your site with clear navigation menus to help users and search engines move through your content effortlessly.
- Ensure your site is responsive, and working flawlessly on both desktop and mobile devices.
Remember, happy users often lead to better engagement, higher rankings, and more conversions.
Technical SEO: Building a Strong Foundation
The goal of technical SEO is to make your website easily discoverable, crawlable, and indexable by search engines. If Google struggles to access your content, it can’t rank you effectively—leading to lost traffic.
Key Elements of Technical SEO
- Site Architecture
A well-structured site architecture organizes your pages into categories, making it easier for users and search engines to navigate.
While architecture isn’t a big concern for a small site with 5 pages, it becomes crucial as your site grows to hundreds or thousands of pages. An intuitive structure improves both user experience and SEO performance.
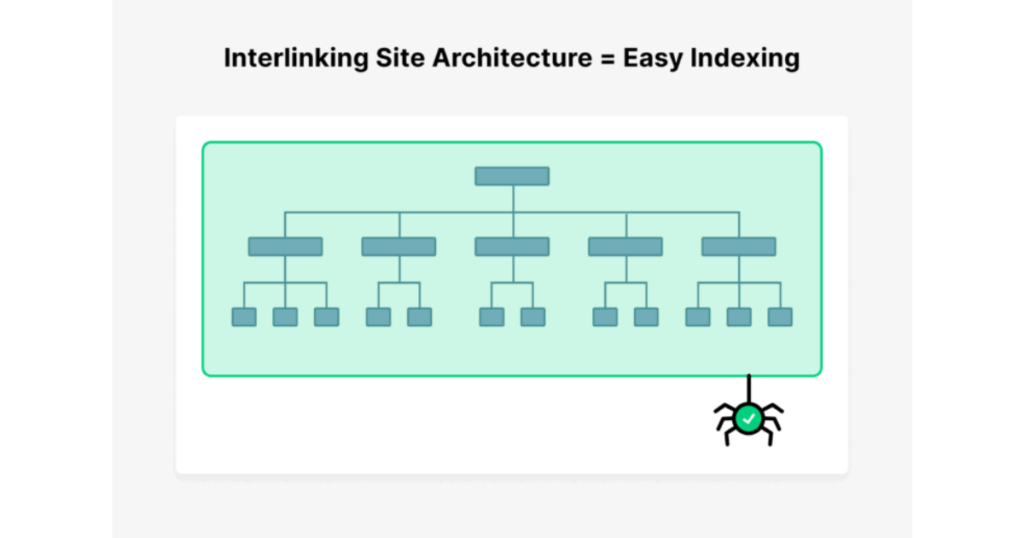
Pro Tip: Internal Linking
Leverage internal links to connect related pages within your site. This not only helps users explore your content but also distributes link equity, boosting the visibility of important pages.
Stay tuned as we dive deeper into more technical SEO tips in the next section!
Internal Linking: Boosting SEO and Navigation
Internal linking is a powerful way to guide users and search engines through your site while improving rankings. Make sure you point internal links to high-priority pages. Ideally, every page on your website should have at least one internal link.
Pro Tip: Use Keyword-Rich Anchor Text
Instead of generic anchor text like “click here,” opt for descriptive, keyword-rich text. For instance, if you’re linking to a page about cold brew coffee, use an anchor like “cold brew coffee guide.”
For more details, check out our guide on How to Set Up an SEO-Friendly Website Architecture.
Optimize for Mobile
In today’s SEO landscape, mobile optimization is essential. Google’s mobile-first indexing means your site’s mobile version is considered the primary version for ranking. Plus, over 60% of web traffic comes from mobile devices.
How to Improve Mobile Friendliness:
- Use a responsive design to ensure your site adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes.
- Avoid intrusive popups or ads, as they can frustrate mobile users.
- Optimize font sizes for readability on small screens.
- Make buttons and menus easy to tap, enhancing usability.
Check your site’s mobile performance using Google’s Core Web Vitals report in Search Console. These metrics evaluate speed, responsiveness, and visual stability.
Measure and Improve Page Speed
A fast-loading site isn’t just user-friendly; it’s an SEO ranking factor. Use Google PageSpeed Insights to evaluate your site’s speed. This tool provides a score (0–100) and actionable recommendations to improve performance.
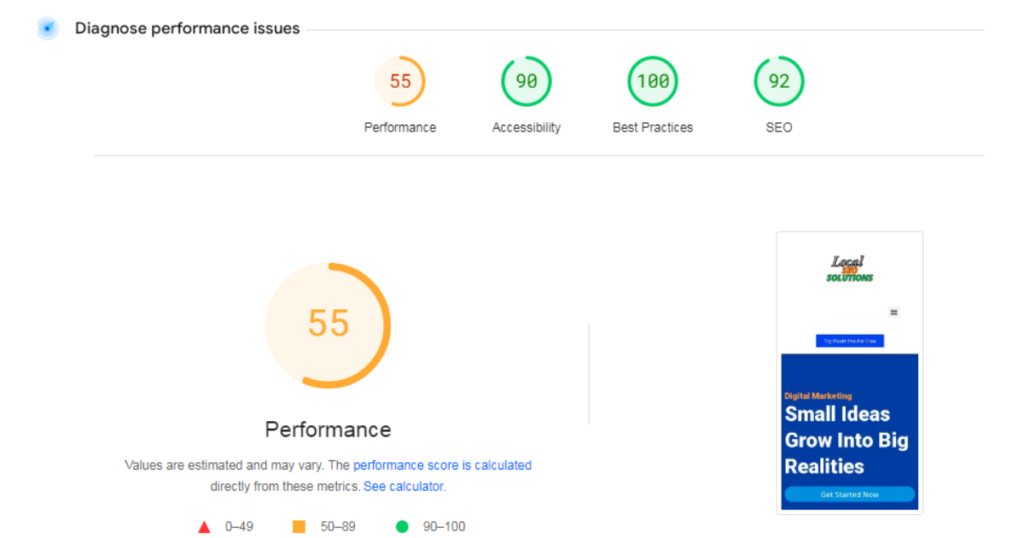
Quick Fixes for Speed:
- Compress images and enable browser caching.
- Use a lightweight theme or optimize your site’s HTML with tools or plugins.
- Consider consulting a developer for more complex fixes.
Secure Your Site with HTTPS
HTTPS not only protects user data but is also a lightweight ranking factor. 99.4% of first-page search results use HTTPS encryption.
If your site isn’t secure, browsers may display warnings, deterring visitors. Ensure your site redirects correctly after implementing HTTPS, as URLs will change.
Off-Page SEO: Building Authority Outside Your Website
Off-page SEO focuses on improving your site’s authority and visibility through external strategies. While it includes local SEO, social media marketing, and digital PR, link building is often the most impactful.
Focus on High-Quality Backlinks
Not all backlinks are equal. Links from authoritative, relevant websites hold more SEO value than those from unrelated or low-authority sites.
- Use tools like Semrush’s Authority Score to evaluate potential link sources.
- Prioritize links from sites related to your industry for maximum relevance.
For example, if your site is about SEO, a link from a reputable SEO blog like Moz carries significant weight.
Proven Link-Building Techniques
- The Skyscraper Technique
This involves creating content that improves upon existing top-ranking pages. Promote your content to sites linking to those pages to gain backlinks. - Guest Posting
Contribute high-quality content to related sites to earn exposure and links.
- Avoid overusing keyword-rich anchor text.
- Limit the number of guest post backlinks in your link profile to avoid spam signals.
- Create Linkable Assets
These are resources that naturally attract links, such as:
- Industry studies
- Visual guides
- Free tools
- Curated resource lists
For example, a comprehensive list of SEO tools can attract links from other blogs and websites in your niche
Getting Started with SEO
Implementing these strategies is a great foundation for SEO success. For further learning, explore these resources:
- How to Do Keyword Research: Step-by-step instructions on finding and targeting the right keywords.
- How to Create SEO Content: Tips for crafting high-ranking, traffic-driving content.
- Google Analytics Mastery: Learn to measure and refine your SEO performance.

By optimizing on-page, technical, and off-page elements, you’ll set your website on the path to sustained growth in search rankings and organic traffic.

Pingback: SEO vs. SEM: A Quick Guide - Local Solutions